Purpose of life –
आयुः कामयमानेन धर्मार्थसुखसाधनम् ।
आयुर्वेदोपदेशेषु विधेयः परमादरः ॥२॥ (AH.Su.1)
Purpose/ Objectives of Life is :
1. Dharma – to determine paths of life
2. Artha – money
3. Kama – desires
4. Moksha – Liberation/ Salvation
Ayurveda Avatarana (hierarchy of Ayurvedotpatti) –
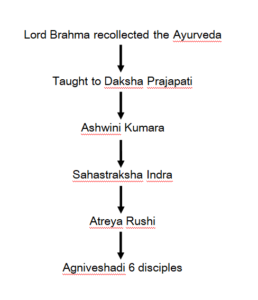
ब्रह्मा स्मृत्वाऽऽयुषो वेदं प्रजापतिमजिग्रहत् ।
सोऽश्विनौ तौ सहस्त्राक्षं सोऽत्रिपुत्रादिकान्मुनीन् ॥३॥
तेऽग्निवेशादिकांस्ते तु पृथक् तन्त्राणि तेनिरे । (AH.Su.1)
Eight branches of Ayurveda –
कायबालग्रह उर्ध्वाङ्ग शल्यदंष्ट्राजरावृषान् ॥५॥
अष्टावङ्गानितस्याहुः चिकित्सा येषु संश्रिता । (AH.Su.1)
Eight branches of Ayurveda :
- Kaya Chikitsa
- BalaChikitsa
- GrahaChikitsa
- UrdhwangaChikitsa
- Shalya Chikitsa
- DramshtraChikitsa
- JaraChikitsa
- VrushaChikitsa
Concept of Tridoshas w.r.t. qualities (Guna), location in body &time period (kaala) –
वायुः पित्तं कफश्चेति त्रयो दोषाः समासतः ॥६॥
विकृताविकृता देहं घ्नन्ति ते वर्तयन्ति च । (AH.Su.1)
There are 3 Dosha :
- Vata
- Pitta
- Kapha
विकृत – देहंघ्नन्ति – In vitiated state, they cause diseases & destroys the body.
अविकृत – देहंवर्तयन्ति – In equilibrium state, they maintain the body in healthy condition.

