Darshana Nirukti –
The word darshan comes from the Sanskrit root “darsh”, which means “to see” or “to observe.” In other words, darshan refers to the act of visually perceiving or witnessing
Darshana Definition –
दृश्यते यथार्थ तत्वं अनेन इति दर्शनम् । (सर्वदर्शनसंग्रह)
Darshana refers to the means through which one can perceive, observe, or comprehend, leading to the attainment of true knowledge. It is the process by which we gain deeper understanding and insight.
Origin of Darshana –
- Darshanas are integral to Indian philosophy, evolving alongside creation and flourishing during the Upanishadic period.
- The Vedas and Vedangas serve as the primary sources for these Darshanas. Over time, the core teachings of all the philosophical texts were consolidated into a comprehensive collection known as Sarva Darshana Sangraha.
Importance of Darshana –
- Provides understanding of the true nature and secrets of creation and its problems.
- Distinguishes between good and bad, truth and falsehood, happiness and sorrow.
- Identifies the causes of human suffering.
- Offers permanent solutions for liberation from suffering.
- Helps eliminate false or illusory knowledge (mithya jnana).
- Provides knowledge of the beyond-worldly actions or the path to self-realization (Atma Vidya) to achieve freedom from suffering.
- Facilitates proper education about the nature of creation.
- Promotes direct realization of the Absolute Truth (Satya-Sakshatakara).
- Enhances both sensory and spiritual perception.
- Tattva knowledge guides one to walk the right path in life.
Analysis of different terms –
Philosophy:
- The term “philosophy” is derived from the Greek word philosophia, meaning “love of wisdom.”
- It is the organized exploration of basic and universal questions related to existence, reasoning, knowledge, ethics, consciousness, and language.
- Philosophy involves examining the core nature of knowledge, reality, and existence.
- It is the logical and thoughtful analysis of reality in its entirety or the fundamental aspects of human life and experience.
- The study emphasizes abstract and systematic inquiry into the essential nature of life and the world.
Spirituality:
- Spirituality refers to a focus on the human spirit or soul, in contrast to material or physical concerns.
- The word spirit originates from the Latin term spiritus, meaning “soul,” “ghost,” “courage,” “vigor,” or “breath,” and signifies the essential life force in humans and animals.
- The term “spiritual” pertains to matters related to the spirit, encompassing the thoughts, actions, and experiences of individuals as they reflect on their relationship with the divine or sacred.
- Spirituality involves personal, inner experiences that connect an individual to a sense of something greater than themselves, often related to the divine.
Religion:
- Religion is defined as the belief in and worship of a higher, often divine, power or being, such as a personal God or gods.
- It is a social and cultural system that encompasses various behaviors, practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, sacred texts, holy places, prophecies, ethics, and institutions.
- Religion typically connects humanity to supernatural, transcendent, or spiritual dimensions of existence.
- It serves as a framework that guides individuals and communities in understanding their relationship with the divine and the universe.
Classification of Darshana –
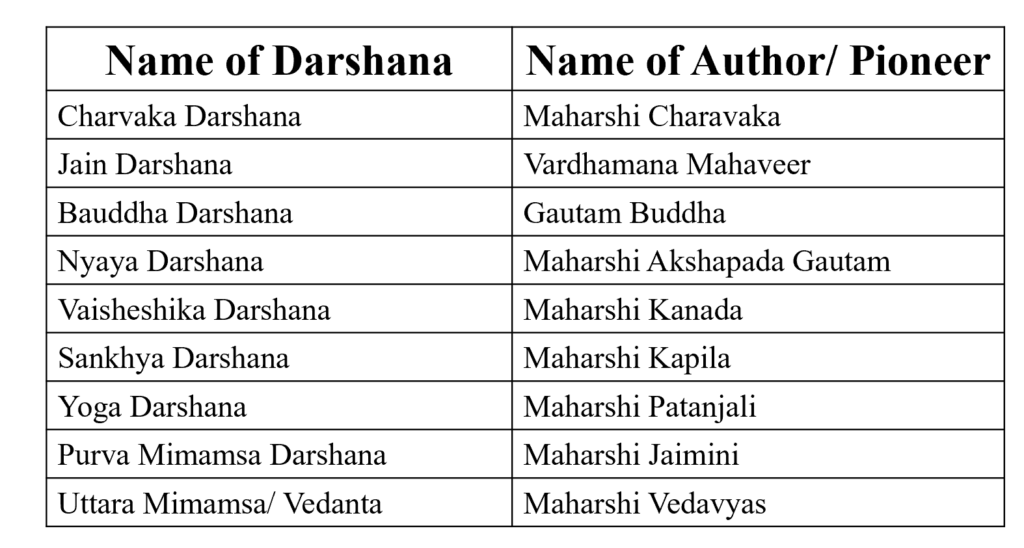
Authors/ Pioneers of Darshana –
Philosophical foundation of Ayurveda –
- The fundamental principles of Ayurveda can be understood through the lens of Indian philosophy (Darshana), which is deeply rooted in human experience and closely connected to life.
- Darshanas are collections of ideas and teachings put forward by various saints and sages, who used heightened sensory perception, extraordinary intellect, and thoughtful discussions to uncover the secrets of creation.
- Darshanas, like Ayurveda, have ancient origins, both emerging during the Upanishadic period.
- Darshanas explore the secrets of creation (Srushti), its evolution, and the processes of creation and dissolution (Srushti-Laya).
- They delve into the concepts of happiness and suffering (Sukha-Duhkha), attachment and detachment (Raga-Vairagya), and the principles of righteousness and unrighteousness (Dharma-Adharma).
- They examine the nature of truth and falsehood (Satya-Asatya).
- Both Darshana and Ayurveda address the soul, mind, and sensory organs.
- Both systems aim to alleviate the threefold suffering (Trividha Duhkha).
- The two are closely interconnected in their teachings.
- Ayurveda incorporates health-related insights from Darshanas.
- The ultimate goal of both is liberation or salvation (Moksha).
- Ayurveda accepts teachings from all Darshanas, considering their suggestions to be valuable.
- Overall, Ayurveda embraces health principles from various Darshanas, regardless of their different classifications.

